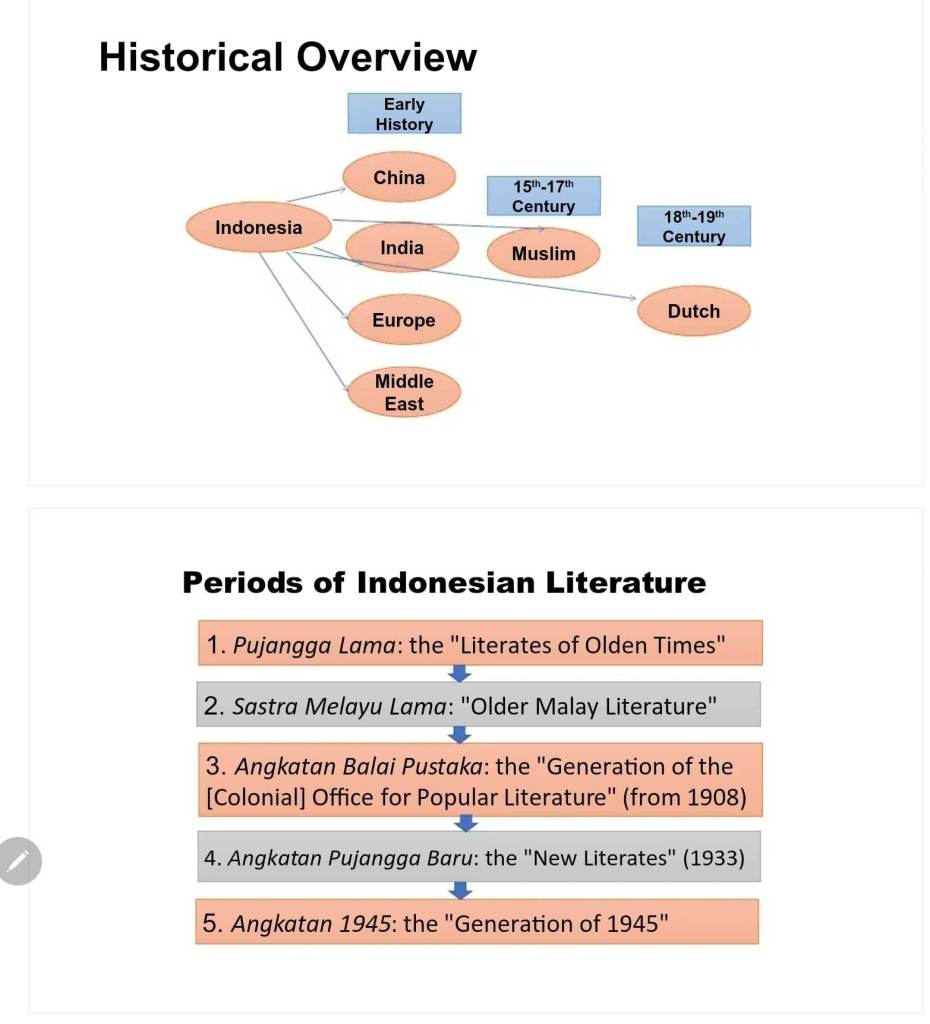
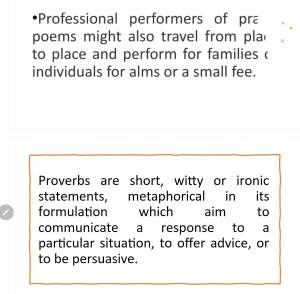
Literature has the power to give us an enriched understanding of other worlds, lives and times, of the way things have been and how they might be. Reading, thinking, writing and talking about literature is both a personal and collegiate experience a model of how society operates or should operate. Studying literature explores the text in its many contexts, how the text finds and makes a place in the world, how it is enabled to speak and to make a difference.
What is Literature?

literature is a body of written works. It has been applied to those imaginative works of poetry and prose distinguished by the intentions of their authors and the perceived aesthetic excellence of their execution. Literature may be classified according to a variety of systems, including language national origin, historical period, genre, and subject matter.
Why do we teach literature?
- Cultural enrichment– reading literature promotes cultural understanding and awareness.
- Linguistic model– literature provides examples of “good” writing, linguistic diversity, expressive ranges and so on.
- Mental training– better than other discipline, literature trains the mind and sensibility.
- Extension of linguistic competence– litertaure stretches the competences of learners who have mastered thelinguistic rudiments.
- Authenticity- Literature is genuine linguistic material, not a linguistically contrived textbook.
- Memorability– Because literature, especially poetry and songs, is memorable, it can be a memorized archive of linguistic usage.
- Rhythmic resource– Poems assist the learner in assimilating the rythms of a language.
- Motivating material– literature is more likely to engage with and motivate a learner than artificial teaching inputs because it is generated by some genuine impulse on the part of the writer and deals with subjects and themes which may be of interest to the learner.
- Convenience– litetarure is a handy resource.
- Memorability– because literature , espicially poetry and songs is memorable, it can be a memorized archive of linguistic usage.
To sum it up studying literature teaches us about the life, cultures and experiences of people in other parts of the world. It gives us information about other parts of the world which you may never be able to visit in your lifetime.
Literature according to Genre

- it came from the Greek word poiesis which means making.
- it refers to those expressions in verse, with measures, rhymes, lines, stanzas and melodious tone.
- poetry is an expressive form of writing. it allows author to share an idea or insight with others in a meaningful way.
- poetry is not written in sentences and paragraphs like prose. instead, it uses different structures that make it interesting to read.
Divisions and Types of Poetry
I. Lyric Poetry– in earlier days, it was meant to be sung to the accompaniment of musical known as lyre.
a. Simple Lyric– embraces a wide variety of poems and is characterized by subjectivity, imagination,melody, and emotion.

b. Song– short lyric poem which has a specific melodious quality and is intended to be sung.

c. Sonnet– a poem expressing of 14 lines with a formal rhyme.

d. Elegy– a poem expressing lament or grief for dead.

e. Ode- most splendid type of lyric poetry.

II. Narrative Poetry– it tells a story following an order of events. it includes:
a. Ballad– short simple narrative poem composed to be sung and is orally told from one generation to another.

b. Metrical Romance– a long rambling love story in verse which is centered around the adventures of knights and lords and their royal ladies during the age of chivalry.
c. Epic- a long majestic narrative poem which tells the adventures of a traditional hero and the development of a nation.
III. Dramatic Poetry– it has the elements that are closely related to drama because it is written in dramatic form or make use of a dramatic technique. It includes:
a. Dramatic Monologue- a combination of drama and poetry which represents the speech of a character in a particular situation at a critical moment.
b. Soliloquy– passage spoken by the speaker in a poem of a character in the play except that there is no one present to hear him except the audience or the reader.
c. Character Sketch- poem which the writer is concerened less with complete or implied matters of a story, but rather with arousing sympathy for, or some interest in an individual.
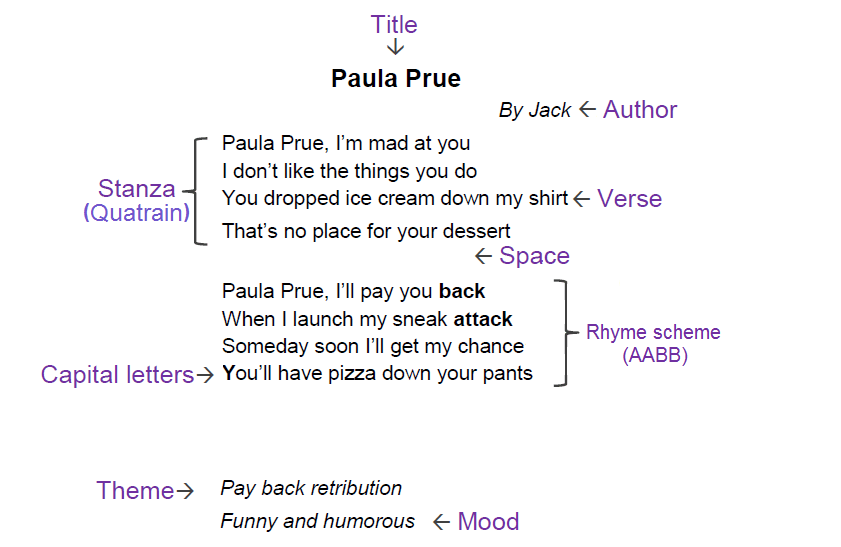
| STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF POETRY |
| 1. Verse– One line of poetry |
| 2. Stanza– group of verses |
| 3. Rhythm– beats or accented syllables |
| 4. Meter- pattern of beats or accented syllables |
| 5. Rhyme- syllables that sound similar |

- it is derived from the Latin word prosa which means straightforward.
- Prose is ordinary language.
- Prose is written in sentences and paragraphs that may include dialogue.
- Most of the literature we read is written in pose.
- it is a form or technique of language that exhibits a natural flow of speech and grammatical structure.
Prose is a style of writing that does not follow a strict structure of rhyming and/or meter. Prose uses normal grammatical structures. Elements of prose writing include regular grammar and paragraph structures that organize ideas, forgoing more stylistic and aesthetic forms of writing found in poetry and lyrics. Prose can include normal dialogue, speeches, novels, news reports, etc. Prose is distinguished from poetry which uses line breaks and has meter that tends to defy normal grammar rules. In today’s literature, most stories are told in prose. There is no longer much emphasis on the oral tradition of storytelling, to which verse was very well suited. Since print came to be commonplace, storytellers tend to rely on prose to tell their stories because of the freedom it allows.
TYPES OF PROSE
- FICTION- this pertains to a narrative form, in any medium, consisting of people, events or places that are imaginary. In other words, it is based strictly on history or fact. Examples: short stories, legend, fairy tale letters, folk tale memoirs, novel, fables, and myth.
- NON-FICTION- it is any document or content that purports in good faith to represents truth and accuracy regarding information, events or people. Examples: essay, report, personal narrative, memoirs,letter, article,journal,biographies
DRAMA
Drama can also be called a play. in a written form, a play includes a cast of characters, dialogue and stage directions. it is organized in scene and acts. The structural elements of drama are:
Cast– list of characters in play. Dialogue– words that tell the actors what to say. Stage Directions– words that tell how the stage should look or what the actors should do.
Through teaching what literature is, and its component could be a way for the learners to live a fulfilling life to think critically and to figure out what the truth is and work through problems. To fully understand what’s going on in the book, readers must pay attention to details, form relationships, and develop their individual ideas. Textbooks are frequently used by teachers to help expand students’ vital thinking skills. They will be nicely prepared for their future careers with this tool.
The most important factors in the enjoyment and embracing literature is the methods of teaching performed by the teacher. When students understand how to approach a literary text, they can develop important capabilities that can help them succeed in a future career. Literature is important to be taught at schools or even universities. By learning it, the students are hoped getting helpful things to their life. Usually when students hear the word literature, soon a thick old book of poems, prose and play and also a bored class come to their mind. Actually it is not true, in teaching literature the teacher can build the joyful situation. So, the students can really involve into the lesson and have fun, and then later they will get something from it. In this blog I will discuss the methods and strategies which can be applied in teaching literature in English classroom.

One methods of teaching literature is the CONTEXTUAL LEARNING. Wherein it is based on a constructivist theory of teaching and learning. Learning takes place when teachers are able to present information in such a way that students are able to construct meaning based on their own experiences. The components of contextual learning are:
-Creating meaningful relationship -Performing a significant job retention -Learning to adjust – Collaboration – Critical and creative thinking -Individual experience – The achivement of a high standard – Using authentic assessment
Contextual learning emphasize the following:
-Problem- solving learning -Authentic instruction -Inquiry based learning -Project-based learning -Worked-based learning -Service learning -Cooperative learning
In this part we are going to apply methods which will benefit both teacher as well as learners. I have chosen a poem entitled ‘The Road Not Taken” by Robert Frost, to become an example of teaching poem.

A. pre-reading– Pay attention to the title. Ask the students whether they can get the whole meaning of the poem before reading it or not (only by looking at the title). Based on the title “The Road Not Taken”, ask the implicit or maybe the explicit meaning that the students got at the glance when they look at the title. You will hear many different ideas from your students.
B. Listening- Ask them to listen to your poem reading. This activity can prepare them to read by themselves and discuss it. And then you can start reading it with good rhythm. The good rhythm shows the abstract feeling from the poem.
C. Becoming familiar with the poem- Hand out the copy of the poem to the students, or just write it down on the white board. But if you have the copy, it is much better than write on the board.
D. Discussion Questions– Remind the students that the questions about poem do not always have “right or correct” answers. So students can answer it freely based on their ideas, experiences and maybe their imaginations. Ask the students such questions like these:
1. What does the title “The Road Not Taken” mean to you?
2. What is the connection between the title and the content?
E. Reading- Ask the students to read the poem by themselves, not only once but several times. So that they can deeply get into the poem and hopefully get into the point that the author purposed to be understood.
F. Writing practice– After they have discussed and read the poem several times, now ask them to make connection between the title and the content, also and their experiences. Ask them to imagine that they are the one in the poem. Then ask them “what can you see?, how do you feel?”. Write a paragraph describing the scene. Use their own words, but feel free to borrow some sights, words and phrase from the poem.
Literature Learning- the aims of literature learning is to widen our knowledge and visions to understand more about some great literary works, famous authors and their thought. It will also make us get acquainted with their ideas, their feelings, and their attitudes towards life, man, nature and God.



To know whether the learners understand fully the topics, an assessment is given. Assessment is defined as a process of gathering data to better understand the strengths and weaknesses of student learning. Assessment should integrate grading, learning, and motivation for your students. Well-designed assessment methods provide valuable information about student learning. They tell us what students learned, how well they learned it, and where they struggled. Procedure which is based on tests is called testing. It is the salient part of assessment in learning. Measurement is the quantifiable part of the testing process, it is required to gauge the efficacy of programs and the growth of students. Without measurement, we do not know what to assess. the evaluation is the culminating ct of interpreting the gathered information for the purpose of making judgement about student’s learning and needs. This forms a part of assessment.
The following are the kinds of Assessment and Evaluation

A formative assessment is a short, low-stakes check that provides both teacher and student with immediate feedback on the student’s comprehension of a learning target. The goal of formative assessment is to monitor student learning to provide ongoing feedback that can be used by instructors to improve their teaching and by students to improve their learning.
Examples of formative assessments include asking students to:
- draw a concept map in class to represent their understanding of a topic
- submit one or two sentences identifying the main point of a lecture
Teaching and studying literature gives everyone enjoyment, and reading great literature exercises our imagination. We enjoy stories, it is a pleasure to meet characters and to live in their world, to experience their joys and sorrows. Discussing what literature is all about will give enough knowledge to the learners especially for those who says studying literature is boring. With the use of effective methods and strategies, teacher will be able to teach and deliver what the topic is all about. Those strategies are the key for the learners to love and embrace literature. And when those method is being applied teacher could assess every learners on how far their understanding is based on the lesson. The teachers will give criteria for every assessment that will be given to the learners.